Agonal breathing, a term that may sound unfamiliar to many, is a critical aspect of understanding and responding to breathing emergencies. Whether you’ve encountered it firsthand or have only heard the term in passing, it is essential to grasp the significance of recognizing and addressing agonal breathing promptly.
Let’s look more closely at agonal breathing, shedding light on its nature, causes, and how it differs from other breathing difficulties. Let’s also examine the necessary steps to take in case you encounter someone experiencing agonal breathing.
What is Agonal Breathing?
Agonal breathing, by definition, refers to a distinct and abnormal pattern of breathing that occurs in individuals who are experiencing a severe medical crisis, often near the point of death. It is characterized by irregular, gasping shallow breaths which may be accompanied by
- snorting
- gurgling
- choking sounds
Unlike normal breathing, agonal breaths are typically ineffective at providing adequate oxygen to the body. Some studies suggest that agonal breathing is painful to experience.
Agonal breathing is commonly seen in emergency situations such as sudden cardiac arrest, severe trauma, or as a result of a serious medical condition that impairs the functioning of the respiratory system. It is crucial to differentiate agonal breathing from other types of breathing difficulties, such as asthma or hyperventilation, as the appropriate response and treatment may vary significantly.
What is the treatment for agonal breathing?
Treatment for agonal breathing primarily focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the condition. As agonal breathing is often associated with a severe medical crisis or life-threatening event, prompt medical intervention is crucial. Here are the key aspects of treatment for agonal breathing:
Activate Emergency Medical Services (EMS):
If you encounter someone exhibiting agonal breathing, immediately call 911 for emergency medical assistance. Dial 911 or ask someone nearby to do so. The presence of trained medical professionals is vital for providing advanced life support and initiating appropriate treatment.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR):
If the person is unresponsive and not breathing or only exhibiting agonal breathing, it is crucial to initiate CPR. Begin by performing chest compressions, followed by rescue breaths if you are trained in CPR. CPR helps to maintain blood circulation and provide oxygen to vital organs until professional medical help arrives.
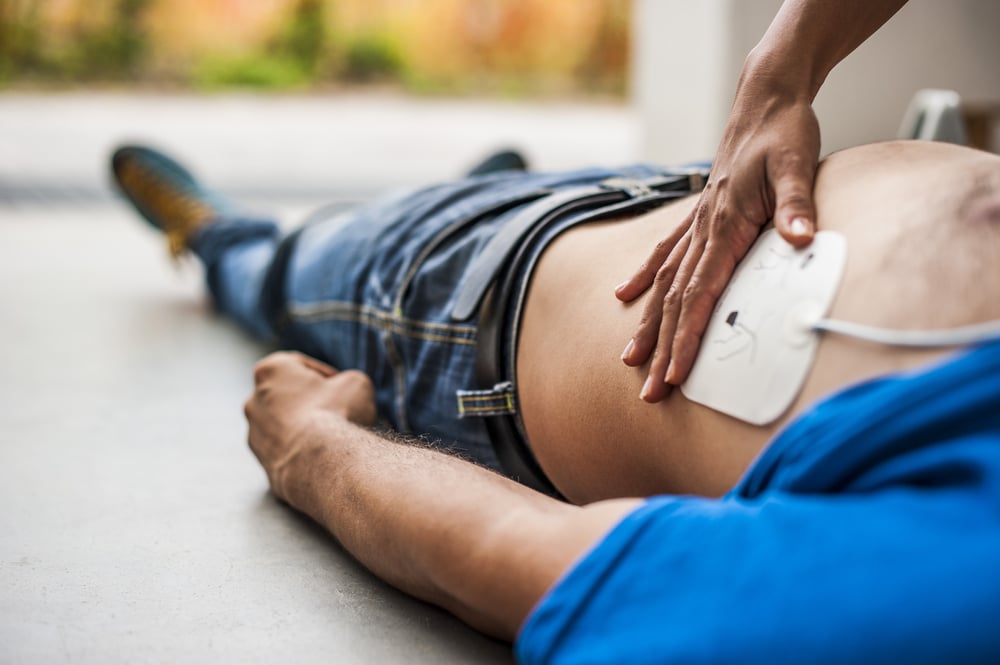
Defibrillation:
In the case of cardiac arrest or certain heart rhythm abnormalities, an automated external defibrillator (AED) may be used to deliver an electric shock to the heart. AEDs are designed to restore normal heart rhythm and can significantly improve the chances of survival when used promptly.
Advanced Medical Interventions:
Once medical professionals arrive, they will assess the situation, perform a comprehensive evaluation, and administer appropriate treatment.
It is important to note that as a bystander, your primary role is to activate emergency services and provide immediate CPR until professional help arrives. Effective and timely medical intervention is critical for the management of agonal breathing and the underlying condition causing it.
To learn how to help agonal breathing, enroll in our Online CPR Class and Certification Training for Healthcare Provider BLS (Basic Life Support) course today!